Limiting reagents and percentage yield worksheet answers – Embark on a comprehensive journey into the realm of limiting reagents and percentage yield with our expertly crafted worksheet answers. This meticulously designed guide unveils the intricacies of these fundamental chemical concepts, empowering you with the knowledge to tackle complex reactions with precision and confidence.
Delve into the essence of limiting reagents, mastering the art of identifying the reactant that governs the extent of a chemical reaction. Discover the secrets of calculating percentage yield, a crucial metric that quantifies the efficiency of chemical transformations. Immerse yourself in a treasure trove of solved problems, gaining invaluable insights into the practical applications of these concepts.
Limiting Reagents
Limiting reagents are reactants that are consumed completely in a chemical reaction, limiting the amount of product that can be formed. To identify the limiting reagent, compare the mole ratios of the reactants to their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation.
The reactant with the smallest mole ratio is the limiting reagent.
Percentage Yield
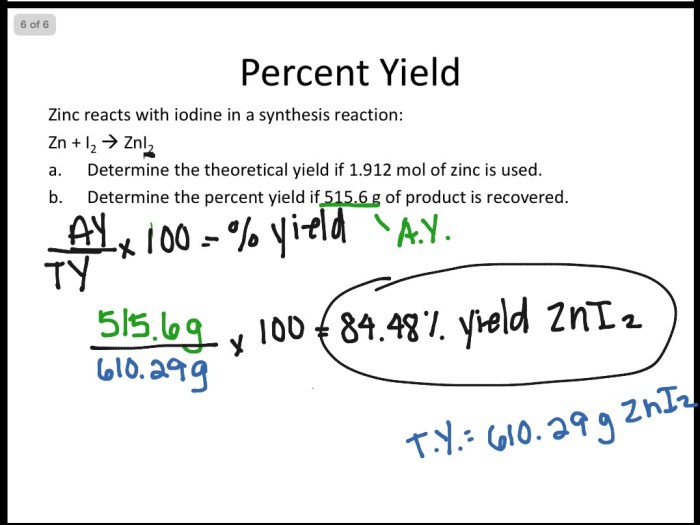
Percentage yield is the ratio of the actual yield of a reaction to the theoretical yield, expressed as a percentage. To calculate percentage yield, divide the actual yield by the theoretical yield and multiply by 100.
Worksheet Answers, Limiting reagents and percentage yield worksheet answers
-*Question 1
In the reaction 2A + 3B → C, 10 moles of A react with 15 moles of B. What is the limiting reagent?Answer:Convert moles to mole ratios:A: 10 moles / 2 = 5B: 15 moles / 3 = 5The mole ratios are equal, so neither reactant is limiting.Question
2:The theoretical yield of a reaction is 50 grams. If the actual yield is 30 grams, what is the percentage yield?Answer:Percentage yield = (Actual yield / Theoretical yield) x 100Percentage yield = (30 grams / 50 grams) x 100Percentage yield = 60%
Additional Examples
Limiting Reagent:* 2 moles of NaOH react with 3 moles of HCl: NaOH is limiting.
4 moles of C3H8 react with 9 moles of O2
C3H8 is limiting.Percentage Yield:* A reaction produces 25 grams of product when the theoretical yield is 35 grams: Percentage yield = 71.4%.
A reaction produces 100 grams of product when the theoretical yield is 120 grams
Percentage yield = 83.3%.
Common Queries: Limiting Reagents And Percentage Yield Worksheet Answers
What is the definition of a limiting reagent?
A limiting reagent is the reactant that is entirely consumed in a chemical reaction, determining the maximum amount of product that can be formed.
How do I calculate the percentage yield of a reaction?
Percentage yield = (Actual yield / Theoretical yield) x 100%
What is the significance of limiting reagents in chemical reactions?
Limiting reagents control the stoichiometry of a reaction, dictating the proportions of reactants and products involved.