In observational learning the most effective models are those – In observational learning, the most effective models are those that embody the principles of imitation and reinforcement. These models provide learners with clear demonstrations of desired behaviors, coupled with consistent feedback and rewards that reinforce those behaviors, leading to enhanced learning outcomes.
Effective observational learning models share several key characteristics. They are:
Observational Learning Models

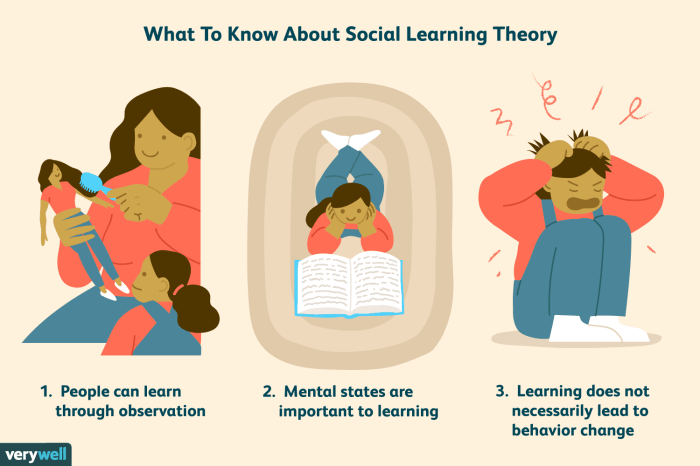
Observational learning is a form of learning where individuals acquire knowledge, skills, and behaviors by observing the actions and consequences of others. Effective observational learning models are characterized by:
- Clarity: Models should provide clear and concise instructions, demonstrations, and explanations.
- Consistency: Models should demonstrate consistent behaviors and outcomes, reinforcing the desired learning.
- Relevance: Models should be relevant to the learner’s goals and experiences, making the learning more meaningful.
- Accessibility: Models should be readily available and accessible to learners, allowing for repeated exposure and practice.
- Feedback: Models should provide feedback on the learner’s performance, helping them identify areas for improvement.
Examples of successful observational learning models include:
- Mentoring programs: Pairing experienced individuals with less experienced individuals to provide guidance and support.
- Apprenticeships: Hands-on training programs where learners observe and work alongside skilled professionals.
- Online courses with video demonstrations: Courses that provide clear and engaging demonstrations of skills and concepts.
Factors that contribute to the effectiveness of observational learning models include:
- Learner characteristics: The learner’s motivation, attention span, and cognitive abilities.
- Model characteristics: The model’s expertise, credibility, and ability to demonstrate skills effectively.
- Contextual factors: The learning environment, including the availability of resources and support.
Role of Imitation and Reinforcement

Imitation is a key component of observational learning. Learners observe and mimic the actions and behaviors of models, acquiring new skills and knowledge. Imitation can be enhanced by:
- Providing clear and specific instructions.
- Breaking down complex skills into smaller steps.
- Creating a safe and supportive learning environment.
Reinforcement is another important factor in observational learning. Positive reinforcement, such as praise or rewards, can strengthen the desired behaviors, while negative reinforcement, such as criticism or punishment, can discourage undesirable behaviors. Reinforcement can be used to:
- Shape desired behaviors.
- Provide feedback on performance.
- Increase motivation and engagement.
Cognitive and Social Factors
Cognitive factors play a significant role in observational learning. Learners need to be able to:
- Attend to and encode the observed behavior.
- Remember and retrieve the observed behavior.
- Decode and interpret the observed behavior.
Social factors also influence observational learning. Learners are more likely to imitate behaviors that are:
- Demonstrated by peers or role models.
- Culturally accepted or valued.
- Associated with positive outcomes.
These factors can be leveraged to optimize observational learning outcomes by:
- Selecting appropriate models.
- Creating a positive and supportive learning environment.
- Encouraging peer collaboration and support.
Practical Applications

Observational learning models have been successfully implemented in various settings, including:
- Education: Teaching new skills and concepts through demonstrations, videos, and simulations.
- Training and development: Developing employee skills through on-the-job training and mentorship programs.
- Social learning: Acquiring social skills and behaviors through observing and imitating others.
- Health and wellness: Promoting healthy habits and behaviors through modeling and reinforcement.
Benefits of using observational learning include:
- Enhanced skill acquisition.
- Increased efficiency and effectiveness.
- Improved motivation and engagement.
- Reduced errors and accidents.
Challenges associated with observational learning include:
- Lack of access to appropriate models.
- Inconsistent or inaccurate modeling.
- Learners’ cognitive limitations.
- Negative social influences.
Future Directions: In Observational Learning The Most Effective Models Are Those
Emerging trends and advancements in observational learning research include:
- Use of technology and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance modeling and feedback.
- Development of personalized learning models tailored to individual needs.
- Exploration of the role of social media and virtual reality in observational learning.
Potential areas for further exploration and innovation include:
- Investigating the impact of cultural and social factors on observational learning.
- Developing new methods to assess and evaluate observational learning outcomes.
- Exploring the use of observational learning to promote positive social change.
Technology and AI have the potential to revolutionize observational learning by:
- Providing access to a wider range of models.
- Delivering personalized learning experiences.
- Automating feedback and assessment processes.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key characteristics of effective observational learning models?
Effective observational learning models are clear, consistent, and provide opportunities for learners to imitate and practice desired behaviors.
How does imitation contribute to observational learning?
Imitation allows learners to observe and replicate the actions of others, providing a concrete model for learning new skills and behaviors.
What is the role of reinforcement in observational learning?
Reinforcement, in the form of positive feedback or rewards, strengthens the association between desired behaviors and positive outcomes, reinforcing those behaviors.



