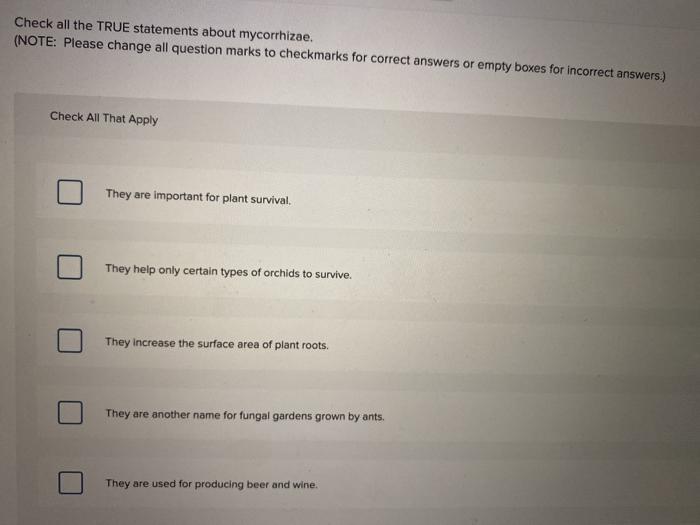
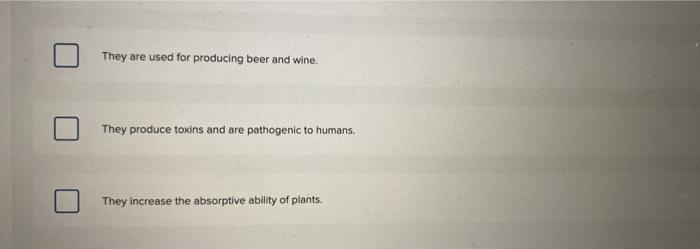
Check all the true statements about mycorrhizae, a symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots, unveils the hidden world of mutually beneficial interactions. Mycorrhizae play a pivotal role in nutrient acquisition, ecological balance, and agricultural practices, shaping the very fabric of our ecosystems.
As we delve into the intricate details of mycorrhizae, we uncover their diverse forms, adaptations, and profound ecological significance. Their ability to enhance nutrient uptake, contribute to soil health, and influence plant succession and community dynamics makes them indispensable players in the intricate tapestry of life.
Definition and Characteristics of Mycorrhizae: Check All The True Statements About Mycorrhizae
Mycorrhizae are symbiotic associations between fungi and the roots of plants. This mutually beneficial relationship involves the exchange of nutrients between the two organisms. The fungus provides the plant with water and essential nutrients, such as phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium, while the plant provides the fungus with carbohydrates and other organic compounds.
Types of Mycorrhizae, Check all the true statements about mycorrhizae
There are two main types of mycorrhizae:
- Ectomycorrhizae: In this type, the fungal hyphae form a sheath around the root tips and extend into the surrounding soil, forming a network of hyphae known as the extraradical mycelium.
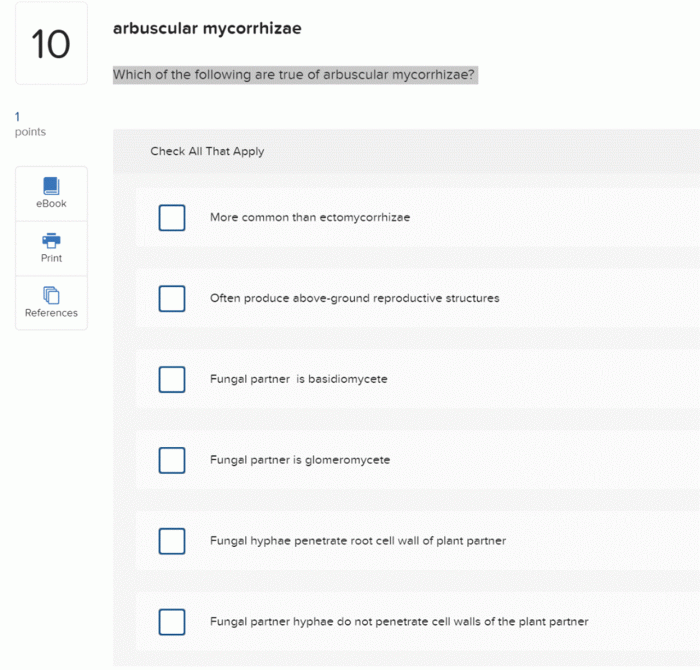
- Endomycorrhizae: In this type, the fungal hyphae penetrate the root cells and form structures called arbuscules within the root cortex.
Morphological and Physiological Adaptations
Mycorrhizae exhibit various morphological and physiological adaptations that facilitate nutrient exchange:
- Increased surface area: The fungal hyphae greatly increase the surface area of the root system, allowing for more efficient nutrient uptake.
- Specialized structures: Ectomycorrhizae form specialized structures called mantles and Hartig nets, while endomycorrhizae form arbuscules, all of which enhance nutrient exchange.
- Nutrient transport proteins: Mycorrhizal fungi produce nutrient transport proteins that facilitate the uptake and transfer of nutrients to the plant.
Popular Questions
What are the main types of mycorrhizae?
Ectomycorrhizae and endomycorrhizae
How do mycorrhizae benefit plants?
Enhanced nutrient uptake, increased drought tolerance, improved soil structure
What is the ecological significance of mycorrhizae?
Contribution to soil health, facilitation of plant succession, support for diverse plant communities
How are mycorrhizae used in agriculture?
Mycorrhizal inoculations to enhance crop growth and reduce fertilizer dependency